Google to Generate Hundreds of Millions of 404 Pages Next Year: Google's Short URL Service goo.gl to Shut Down Completely on August 25 Next Year
In 2009, Google launched its short URL service, goo.gl, to help developers create short links for easy sharing of content across different platforms. At that time, the internet was in a phase of rapid development, and tech companies were launching their own short URL services for use with their products.
However, as time passed, Google gradually phased out the short URL service. In 2018, Google announced it would be shutting down its short URL service, recommending developers use Firebase Dynamic Links or third-party short URL services instead.
By 2019, Google formally discontinued the short URL service, making it impossible to use goo.gl to shorten URLs further. However, existing URLs continued to redirect and access normally, a situation that has persisted for 5 years.
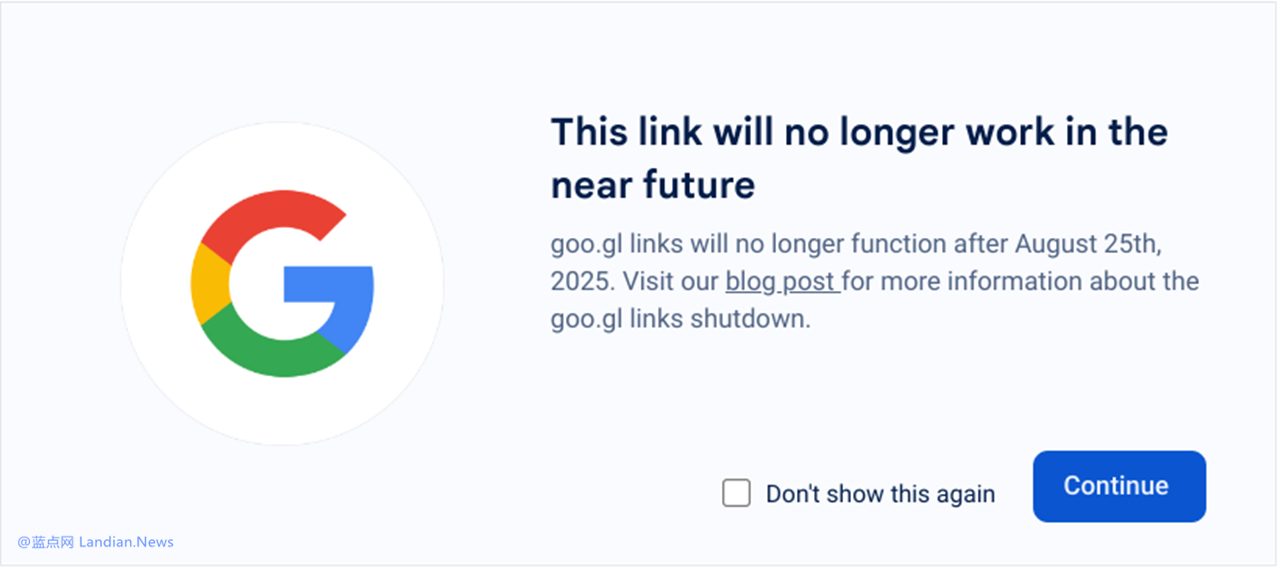
Yet, all good things must come to an end. Google announced today that by August 25, 2025, it will completely shut down the short URL service. All existing short URLs will eventually become HTTP 404 statuses, meaning they will no longer redirect to the target websites.
Starting from August 23, 2024, Google stated that goo.gl short URLs will gradually introduce an intermediary page to remind users that the link will become invalid in the future. More and more short URLs will display this intermediary page over time.
Notably, Google has added a query parameter. If users find the intermediary page reminder annoying or disruptive, they can append the query parameter si=1 to the end of the short URL link to bypass the intermediary page, allowing for direct access until the 404 status is implemented.
After August 25, 2025, these links will become inaccessible. Given the widespread use of Google's short URL service, its shutdown could result in hundreds of millions of new 404 pages on the internet.
Considering that most developers and users who have used Google's short URL service are unlikely to go back and modify their published content to replace the addresses, these 404 pages could pose a nuisance to future visitors. However, this is a common occurrence on the internet; many web pages from before 2010 are already in a 404 status. Unless indexed by the Internet Archive, most of these 404 pages are unable to retrieve their original content.