[Security Guide] What is Password Spraying and How to Counteract Password Spray Attacks?
Recently, there has been a significant increase in password spraying attacks, one of the most notable cases being the attack on some Microsoft employees and executives, where hackers successfully gained account access, leading to a security incident.
Password spraying can be considered a form of brute force attack, but unlike targeting a single account, it targets a specific login system.
Brute force attacks generate a vast number of passwords and attempt to log in frequently to find the correct password. However, security systems now temporarily lock accounts after several failed login attempts, making brute force attacks increasingly impractical.
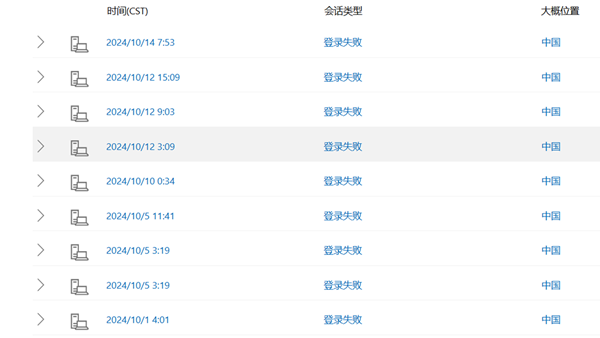
Password spraying typically targets specific systems. Hackers collect a large number of user account details, such as email addresses, and then gather common passwords like "Password12345." They then attempt to log into many accounts with these passwords. This does not trigger security system alarms because it's seen as a normal login error for individual accounts. However, among hundreds of thousands or even millions of accounts, some are likely to use such common, weak passwords, allowing hackers to gain access.
This attack method is akin to watering a lawn with a sprinkler, hence the industry term "password spraying." While not a new tactic, it has become increasingly popular.
How to Prevent and Counteract Password Spraying Attacks?
There are mainly three ways to prevent these attacks: avoid account information leaks (which might be challenging for users), refrain from using weak passwords, and enable MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication).
Enabling MFA is perhaps the most effective measure. Even if hackers obtain a password, without the MFA code or confirmation action, they cannot log in.
Of course, not using weak passwords is also crucial. Simple and easily guessable passwords are always at risk of being cracked.
Another method is countering MFA Fatigue Attacks, which have been prevalent among Microsoft accounts. In an MFA Fatigue Attack, hackers continuously send login requests, leading to users receiving constant notifications and potentially approving the login request out of fatigue or decreased judgment.
Microsoft has enhanced its policy against MFA Fatigue Attacks by requiring a corresponding number to be clicked during a password or passwordless login request for MFA, making it difficult for hackers to succeed without knowing the number.
Fatigue attacks on other account systems have not been widely reported yet, but it could become a trend. If you receive constant login requests, remember to change your password promptly.