Invisible Watermarks: OpenAI's Solution to Detect AI-Generated Content
OpenAI has announced that it has joined the C2PA (Content Authenticity Initiative) alliance's steering committee, alongside other industry leaders, to develop standards for digital content authentication and tracing.
C2PA, founded by software companies, camera manufacturers, and online platforms, aims to add information about the origin of digital products, including images, videos, and audio, to reduce the spread of misinformation.
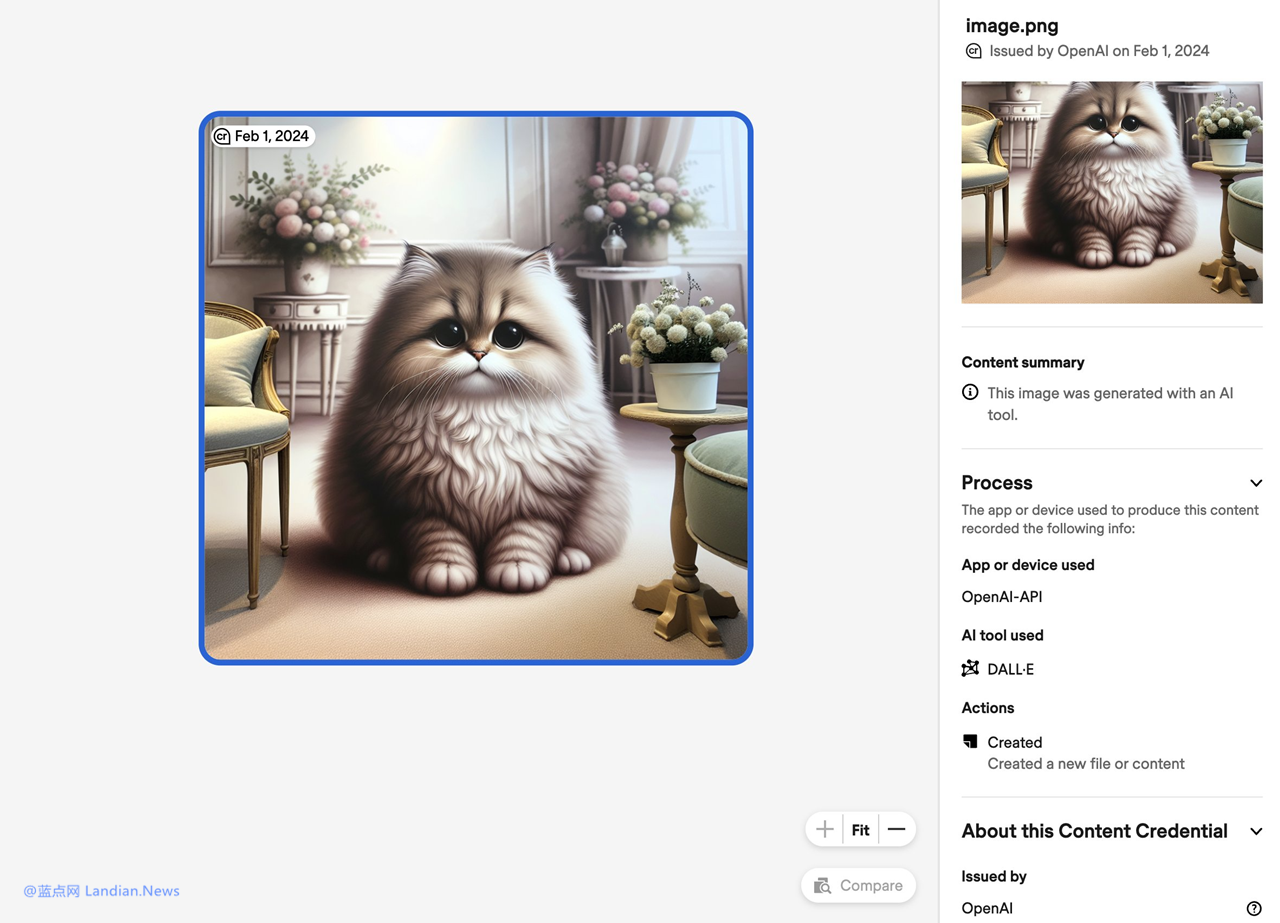
Earlier this year, OpenAI integrated C2PA standards into its DALL-E 3 image generation model, which marks generated images as coming from the model, proving they were created by AI.
OpenAI plans to add C2PA metadata to videos generated by its Sora text-to-video model, allowing users to identify whether a video was generated by Sora or is a real recording.
Notably, C2PA metadata can be deleted, for example, by modifying the image metadata or taking a screenshot of a DALL-E 3 generated image. To address this, OpenAI is preparing to add invisible watermarks.
Invisible watermarks, also known as blind watermarks, are imperceptible to the human eye but can be detected by special tools. OpenAI plans to implement blind watermarks in the future, using difficult-to-delete invisible signals to mark audio and other digital content.
To complement the invisible watermarks, OpenAI will also provide detection tools. The company has developed a classifier to detect AI-generated content, which is now available to some researchers. The tool can detect DALL-E 3 generated images with an accuracy of 98%, with less than 0.5% of non-AI generated images being mislabeled as AI-generated. OpenAI will continue to optimize the tool in the future.