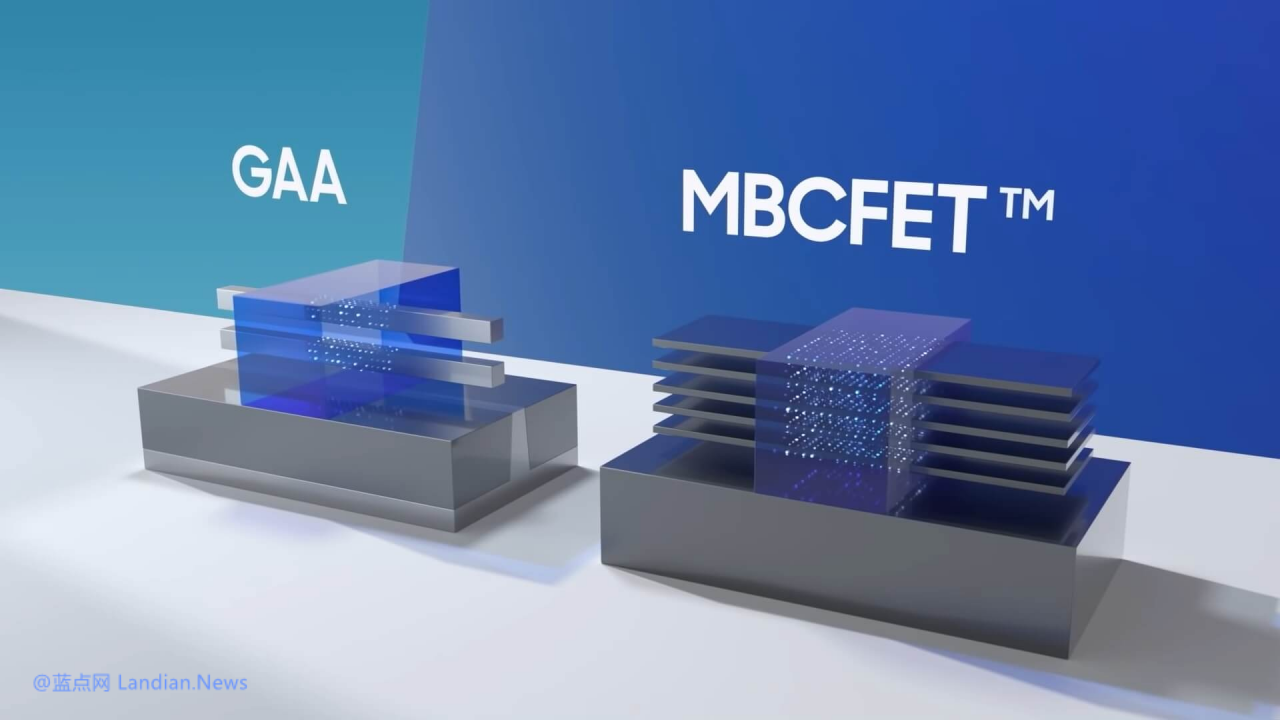
Samsung Dissolves Its Chip Foundry Development Division, Shifting Focus to Enhancing 3nm Process Yield Instead of Pursuing 2nm
Samsung’s advanced process chip foundry division, a key competitor to TSMC, has been dissolved due to its technological development capabilities being inferior to TSMC’s, as well as considering the practical business situation. Samsung has decided to disband the chip foundry technology development department.
According to reports from the South Korean media, following the dissolution of the chip foundry technology development team, its members have been reassigned to other teams, focusing on mass production management, mass production, and process design.
The primary role of the chip foundry technology development department was to support foundry customers, including the development of chip foundry technologies and designing foundry solutions for clients. However, the issue lies in Samsung's low yield rate for the 3nm process.
Previous reports indicated that Samsung’s yield rate for the 3nm process was a mere 10%, leading to the shutdown of some production lines and a significant increase in foundry costs. Continuing in this manner would render the development of 2nm and 1.4nm processes somewhat moot, as the low yield rate would make profitability challenging.
If these reports are accurate, Samsung's originally planned 1.4nm process for 2027 might also be delayed, potentially falling further behind TSMC. However, solving the 3nm process yield rate issue could still be beneficial for the company's revenue.
Samsung plans to reduce its workforce by 30% by the end of the year, with the layoffs being related to the foundry yield rate. Therefore, dissolving the chip foundry technology development department and focusing on improving the 3nm process yield rate might not be a bad move.
Currently, TSMC remains a major player in advanced process technology, having revealed that its roadmap remains unchanged. For instance, the A16 process, referring to the 1.6nm process, is expected to enter mass production by the end of 2026.