Google Bard AI Adds Image Support: A Leap Towards Multimodal Interaction
In the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI), continuous innovation is the key to staying relevant. Following this motto, Google is introducing image support for its Google Bard AI conversational bot, marking a crucial step in its development journey.
Image support in a conversational AI system has been long-desired by users worldwide. The latest update from Google makes this a reality, allowing users to prompt Bard to find images through natural language commands. This functionality aims to foster enhanced communication between the AI and its users, moving beyond simple text-based exchanges.
Given Google's expansive image search index, the integration of image support may not come as a surprise to many. The approach is akin to that of Bing Chat, which utilizes Bing's image search functionality for a similar purpose.
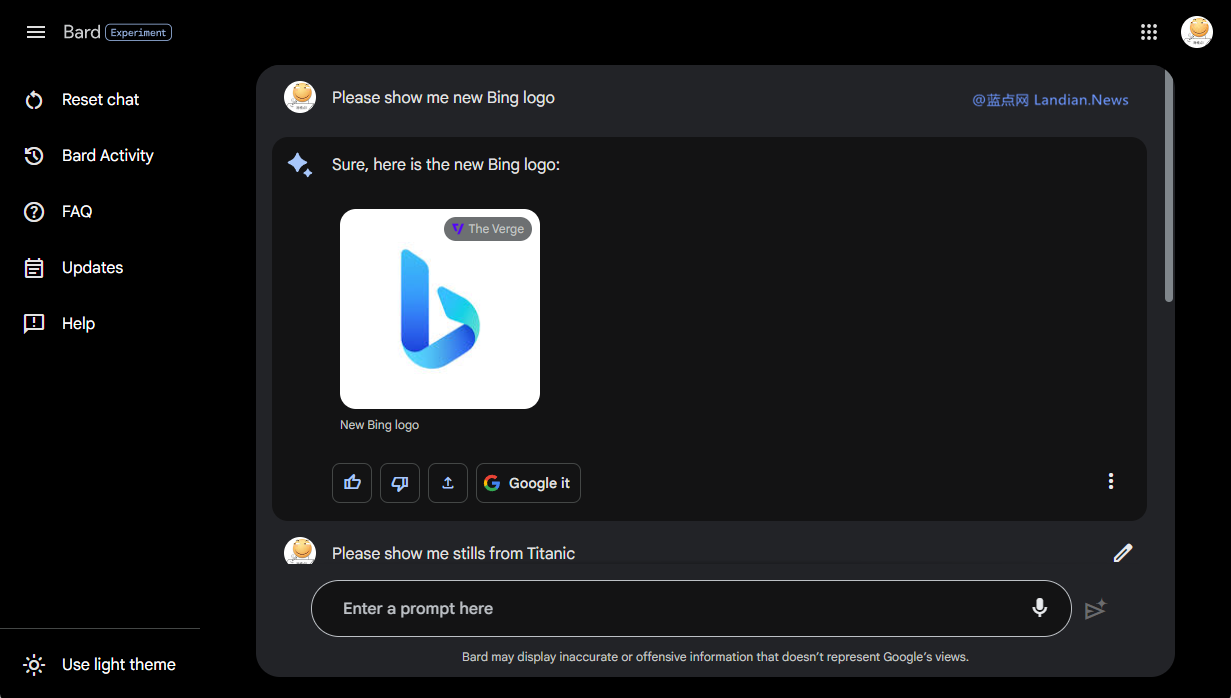
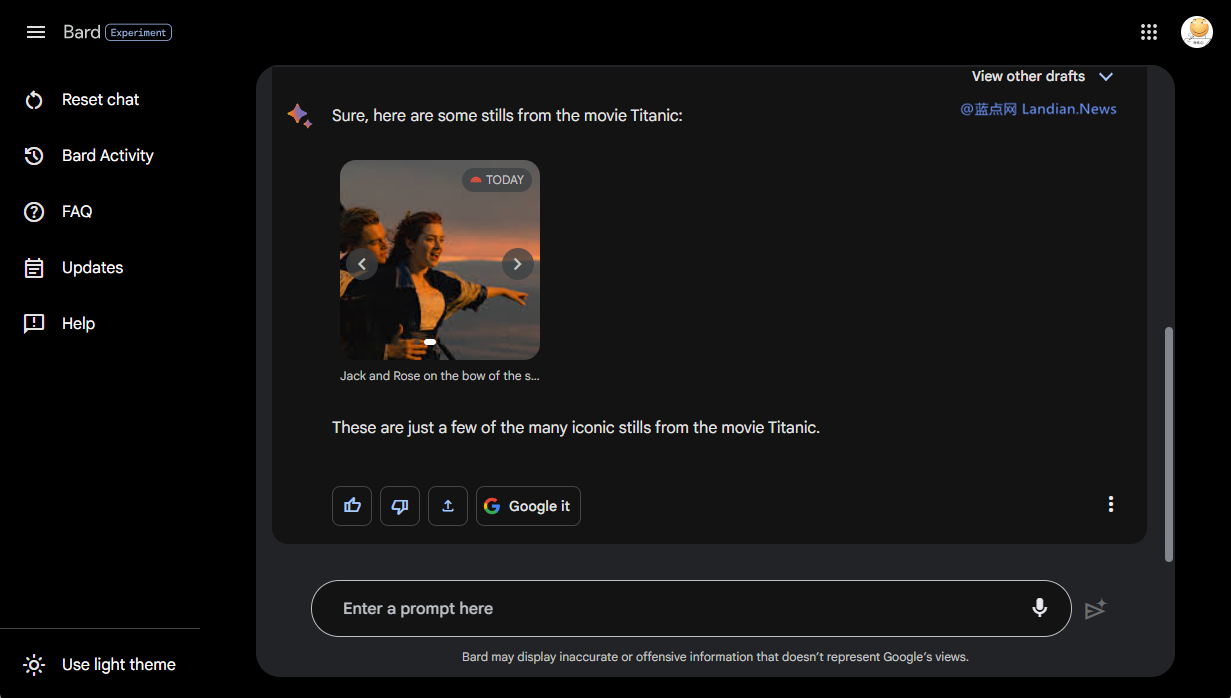
According to Google, the introduction of image support is designed to make ideas more tangible, lending more credibility to Bard's suggestions. It also offers users a richer visual experience during interactions, rather than limiting the exchange to mere text.
However, there's a catch: the image search functionality currently only supports English. The Google Bard itself is still limited to English, Japanese, and Korean, with other languages currently being tested for future support. The decision to start with English for such new features is understandable, but the slow pace of language diversification has raised a few eyebrows considering Google's recognized strength in handling language content.
In contrast, Bing Chat seems to be a step ahead, integrating not just Bing image search, but also OPENAI's DALL-E, which can generate images based on prompt words. Google Bard's journey is an ongoing one, and it remains to be seen how it will step up its game to meet user expectations and match the competition.
In the ever-evolving AI landscape, advancements like these demonstrate the potential for further innovation. With Google continuing to add more layers to its AI, it is clear that the future of human-AI interaction is bound to be increasingly sophisticated and dynamic.