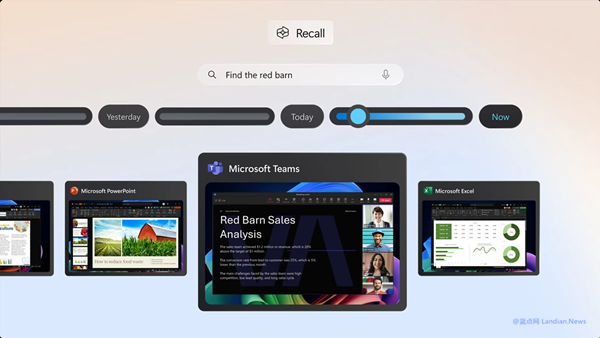
Microsoft is improving the WSL, with the new version set to support mirroring the host machine's network interface and utilizing external DNS.
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a subsystem feature developed by Microsoft for Windows 10/11, allowing users to install Linux systems and related environments on Windows. This capability is particularly beneficial for developers looking to build Linux-based development environments for their projects.
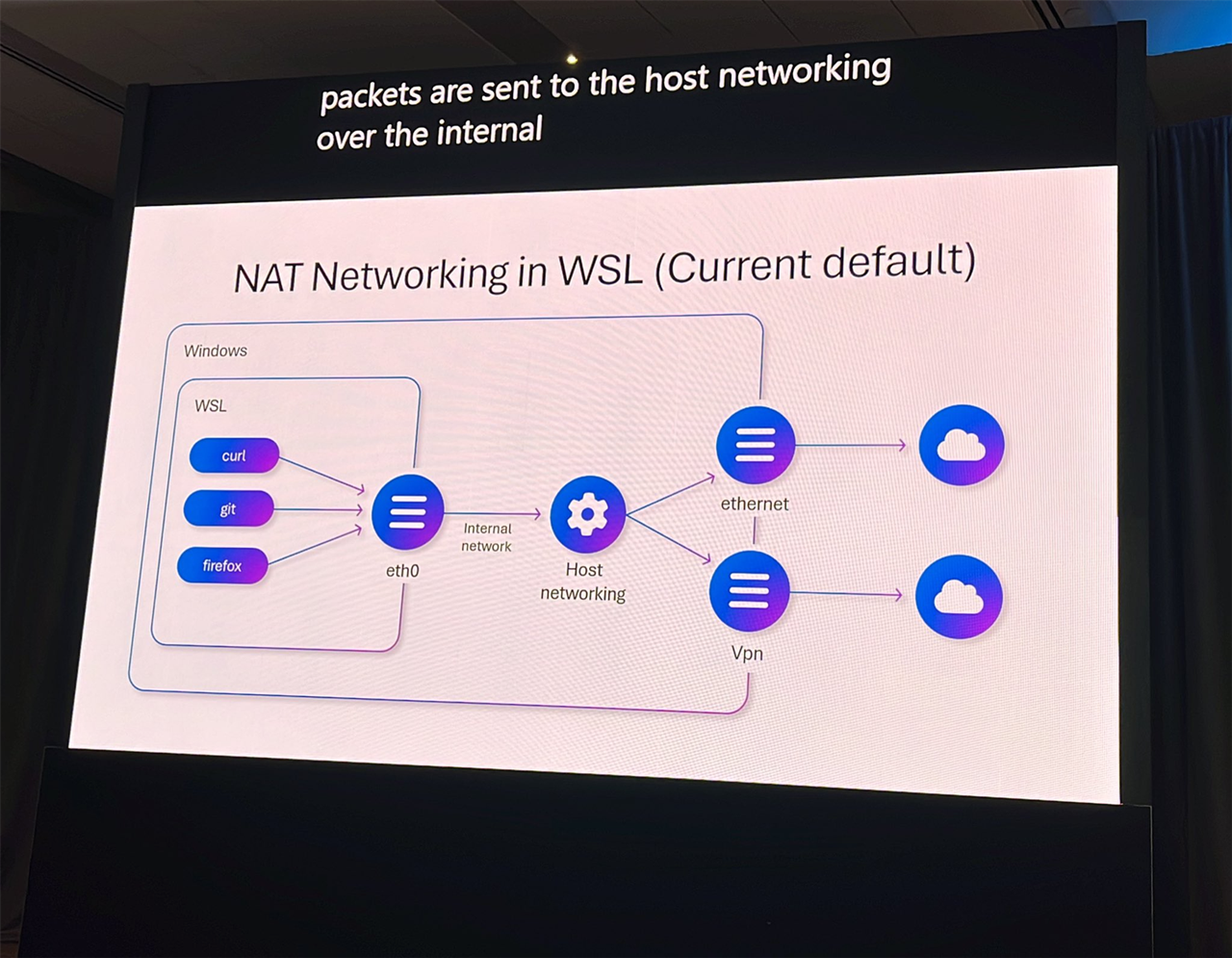
However, WSL has had its share of limitations, notably its default support only for NAT networking. While it's possible to assign IP addresses through certain methods, the process is complex and often requires switching virtual network cards.
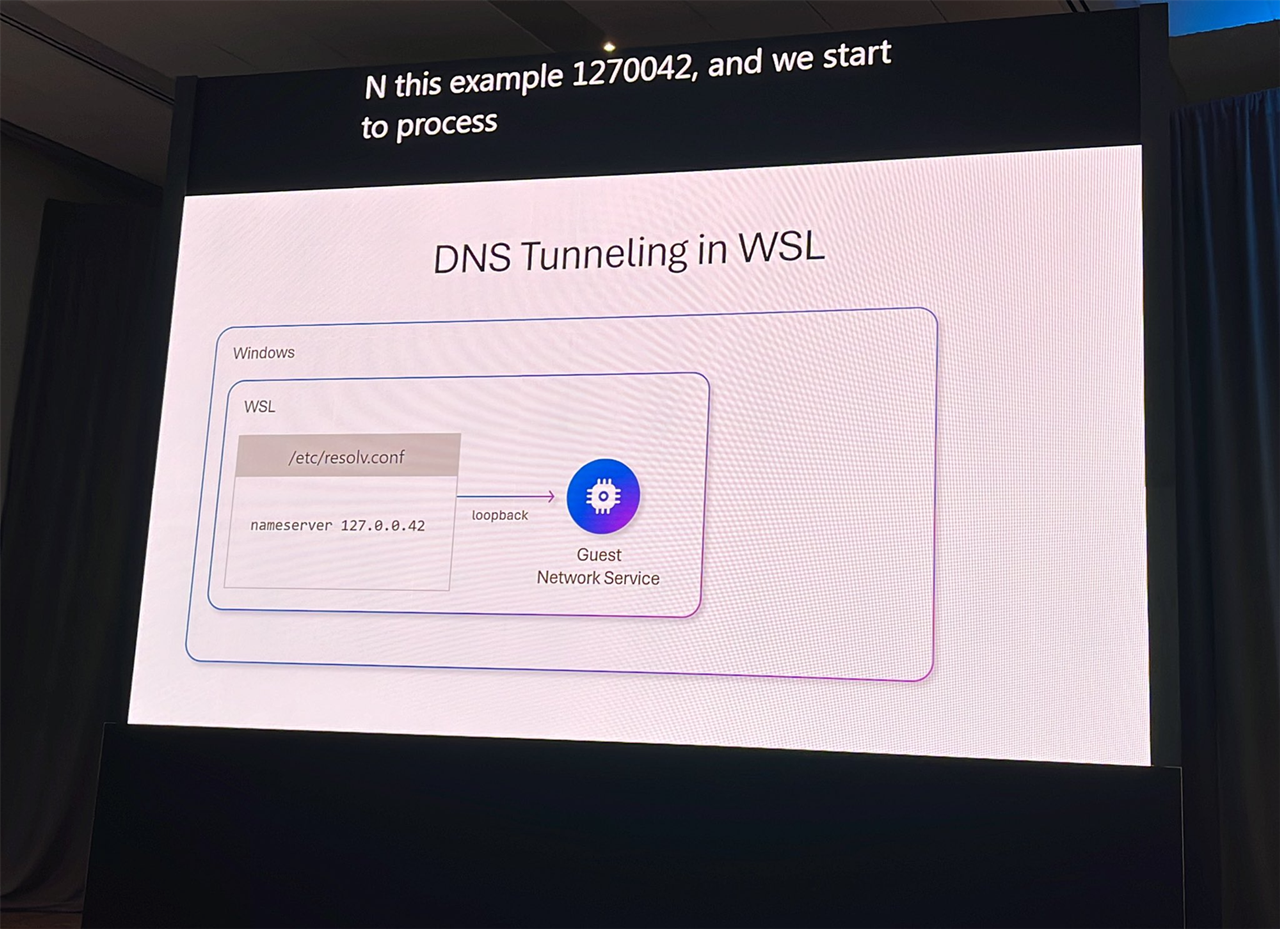
Another issue has been the inability for developers to customize DNS servers within WSL. By default, WSL inherits Windows DNS settings, which, in a corporate environment, might be subject to various DNS security features.
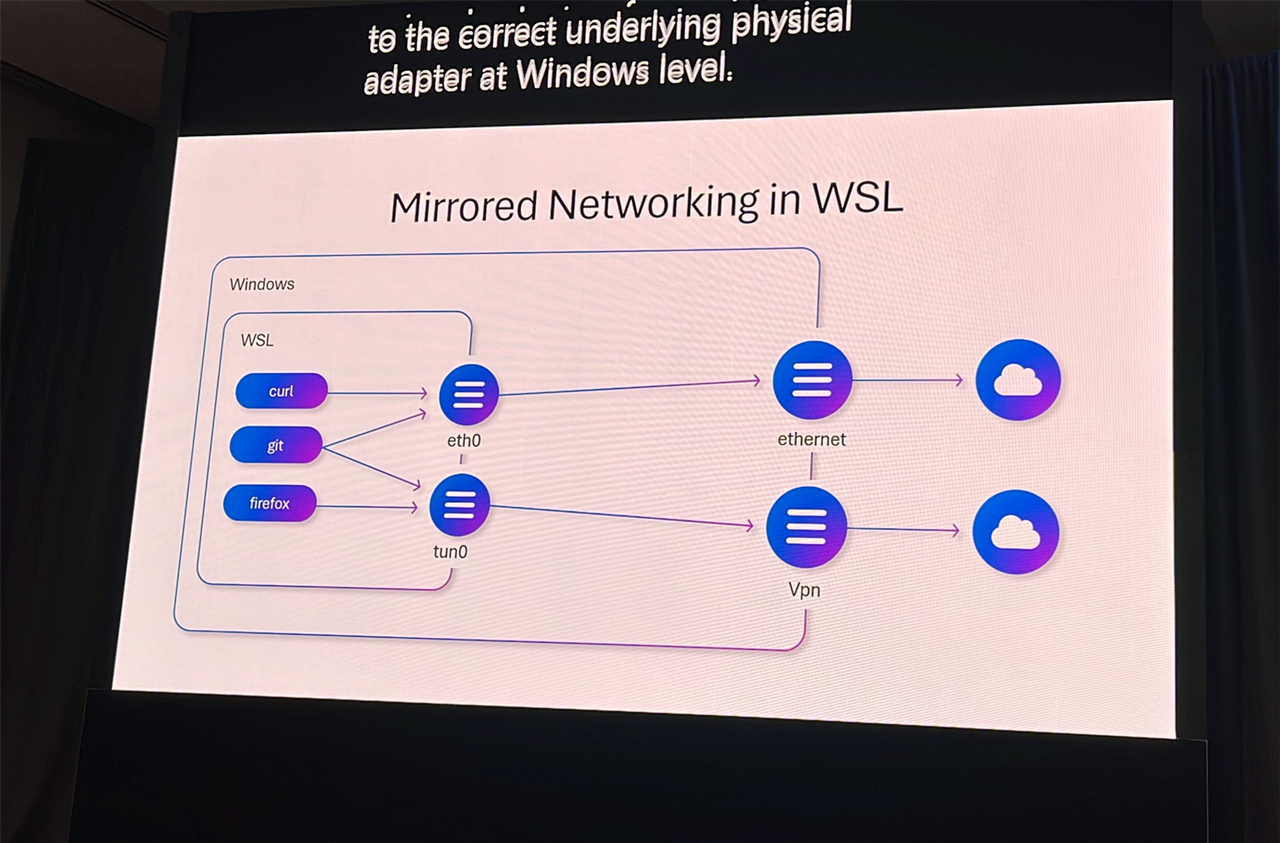
Microsoft is now addressing these developer criticisms by enhancing WSL's capabilities, including those related to NAT networking and DNS settings. The improvements allow WSL to be configured to mirror the host machine's network, managed via routers and switches, and also enable the customization of DNS servers for testing purposes or to circumvent internal DNS security restrictions.
Notably, with the upcoming updates, developers will be able to configure WSL for mirrored networking, select network exits, support IPv6 addresses and LAN services, and even use two modes simultaneously for specific applications, switching between them as needed.
The DNS improvements primarily include support for DNS tunneling, enabling the use of guest network services to set external DNS addresses. This feature allows for the customization to any DNS, bypassing certain security policy restrictions.
These new features will be released in the upcoming WSL update. Developers interested in these enhancements are advised to keep an eye on the Microsoft developer blog for the latest news from Build 2024 in the coming days.



![[Beta Version] Rufus v4.6 Now Supports Bypassing Windows 11 Restrictions Locally Without Needing to Reinstall the System](https://img.lancdn.co/news/2024/06/3684T.png)